I’ve worked with enough small development teams to know the persistent challenge they face. Code review is essential for quality and knowledge sharing, but limited team size means reviews often become bottlenecks or get rushed. When the same three developers review each other’s code constantly, patterns get missed and quality drifts.
I’ve found that AI code review tools address this gap by providing consistent, thorough analysis that complements human review. These tools catch common issues, enforce standards, and surface potential problems before human reviewers spend time on basic checks. The result I see is faster review cycles and more focused human attention on design and logic questions that AI cannot evaluate.
What AI Code Review Actually Delivers
In my experience, modern AI code review goes beyond traditional static analysis. While static analyzers check for syntax errors and known anti-patterns, the AI-powered tools I use understand code context and can identify subtle issues.
Capabilities I’ve seen from AI code review:
- Contextual suggestions - Recommendations consider surrounding code, not just isolated lines
- Natural language explanations - Issues explained clearly, not just flagged with error codes
- Security vulnerability detection - Identification of potential security risks based on code patterns
- Performance recommendations - Suggestions for more efficient implementations
- Code style consistency - Enforcement of team conventions beyond linting rules
- Documentation suggestions - Recommendations for comments and documentation improvements
- Test coverage analysis - Identification of untested code paths
The AI component enables these tools to understand intent and suggest improvements that static rules cannot express.
Comparing Leading AI Code Review Tools
I’ve tested several capable options that serve different needs and integrate with various development workflows. Here’s my breakdown.
GitHub Copilot for Code Review
GitHub Copilot has expanded beyond code completion into pull request review. I find the integration leverages the same models that power code suggestions effectively.
Key capabilities:
- Automatic PR summarization
- Inline suggestions during review
- Security vulnerability flagging
- Natural language explanations of changes
- Integration with existing GitHub workflows
What I like: Native GitHub integration eliminates setup friction for teams already on the platform. The same AI that helps write code can evaluate it, providing consistent context. PR summaries help my reviewers understand changes quickly.
What to consider: It requires GitHub Enterprise or Copilot Business subscription for full review features. Teams on other platforms need alternative solutions.
Pricing: Copilot Business runs approximately $19 per user monthly, with code review features included in the subscription.
CodeRabbit
I’ve had great results with CodeRabbit, which provides dedicated AI-powered code review as a standalone service that integrates with major Git platforms.
Key capabilities:
- Automatic review comments on pull requests
- Security and performance analysis
- Code quality scoring
- Review summary generation
- Custom review rules and preferences
- Support for GitHub, GitLab, and Azure DevOps
What I like: CodeRabbit focuses exclusively on review quality, providing more detailed analysis than general-purpose tools. The platform supports custom configurations that I can align with team standards. Multi-platform support accommodates diverse tooling choices.
What to consider: As a third-party service, CodeRabbit requires additional vendor management. I advise teams to evaluate data handling policies for their compliance requirements.
Pricing: Free tier for open-source projects. Paid plans start around $15 per user monthly for private repositories.
JetBrains Qodana
For teams using JetBrains IDEs, I recommend looking at Qodana, which combines traditional static analysis with AI-enhanced capabilities.
Key capabilities:
- Deep static analysis across many languages
- Integration with JetBrains IDE inspections
- CI/CD pipeline integration
- License compliance checking
- Code coverage integration
- Self-hosted deployment option
What I like: Teams invested in JetBrains tooling get seamless integration. The analysis engine benefits from years of JetBrains inspection development. Self-hosted options address data residency requirements I often encounter with clients.
What to consider: Full benefit requires JetBrains IDE usage. Teams on VS Code or other editors miss some integration advantages.
Pricing: Cloud version includes free tier. Ultimate features and self-hosted deployment require paid licenses.
Amazon CodeGuru Reviewer
For my AWS-focused clients, I often recommend CodeGuru Reviewer for AI-powered analysis integrated with AWS development workflows.
Key capabilities:
- Automatic analysis on pull requests
- Security vulnerability detection
- AWS best practice recommendations
- Integration with CodePipeline and CodeCommit
- Support for Java and Python primarily
What I like: Native AWS integration simplifies adoption for teams already on the platform. Security recommendations reflect AWS security expertise.
What to consider: Language support is more limited than other options. I find it provides the strongest value for Java applications running on AWS.
Pricing: Pay-per-use pricing based on lines of code analyzed. Can be cost-effective for smaller codebases.
Integration Patterns I Use for Small Teams
Effective AI code review fits into existing workflows without creating new friction points. Here are the patterns I implement most often.
Pull Request Integration
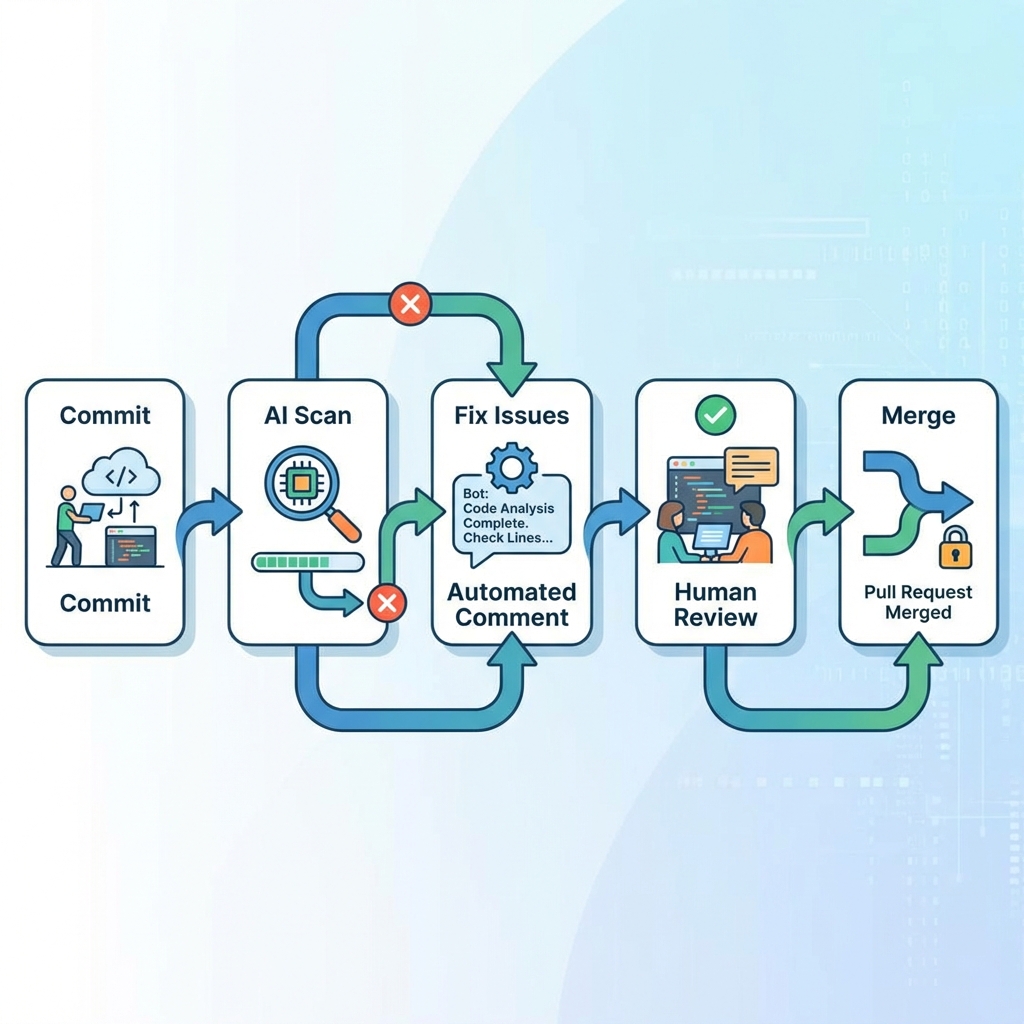
The most common pattern I use triggers AI review when pull requests open or update:
- Developer opens PR with changes
- AI review service analyzes the diff
- Comments appear as review feedback on the PR
- Developer addresses AI suggestions
- Human reviewer sees AI comments alongside their own review
- Approval considers both AI and human feedback
This pattern works with minimal workflow changes. AI comments look and function like human review comments.
Pre-Commit Hooks
I also set up pre-commit hooks to catch issues before code reaches the repository:
# .pre-commit-config.yaml example
repos:
- repo: local
hooks:
- id: ai-review
name: AI Code Review
entry: scripts/ai-review-check.sh
language: script
types: [python]Pre-commit hooks provide faster feedback but require local tooling setup. I find them best used for critical checks that should never reach the main branch.
CI Pipeline Integration
I add AI review as a pipeline stage alongside tests and linting:
# GitHub Actions example
jobs:
ai-review:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v4
- name: Run AI Code Review
uses: coderabbit/ai-review-action@v1
with:
github-token: ${{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }}Pipeline integration ensures every change receives analysis regardless of local developer setup.
How I Maximize Value from AI Review
Raw tool adoption delivers some benefit, but I’ve found that intentional practices multiply returns.
Configure for Team Standards
Out-of-the-box AI review applies generic best practices. I always customize to align suggestions with team conventions:
- Specify preferred formatting and naming conventions
- Set severity levels for different issue types
- Define which files or patterns to ignore
- Configure language-specific rules
- Add custom rules for domain-specific patterns
My investment in configuration reduces noise and increases signal in AI recommendations.
Establish Triage Guidelines
Not every AI suggestion warrants action. I help teams establish clear guidelines:
Always address:
- Security vulnerabilities
- Memory leaks and resource handling
- Breaking changes to public APIs
Usually address:
- Performance improvements with clear impact
- Code clarity suggestions improving readability
- Documentation gaps for public interfaces
Evaluate case-by-case:
- Style preferences beyond configured standards
- Alternative implementations with similar outcomes
- Suggestions requiring significant refactoring
Document exceptions:
- When AI suggestions are intentionally ignored
- Rationale for non-standard patterns
I find clear guidelines prevent both dismissive rejection and unthinking acceptance of AI feedback.
Use AI to Train Junior Developers
I’ve found that AI review feedback serves as continuous education:
- Explanations teach concepts junior developers might miss
- Consistent feedback reinforces standards
- Security suggestions build awareness of vulnerability patterns
- Performance recommendations develop optimization intuition
I encourage treating AI suggestions as teaching moments rather than just items to address.
Track Improvement Over Time
I always measure whether AI review delivers value:
- Issues caught before human review
- Time saved in review cycles
- Bug density changes post-deployment
- Developer satisfaction with review process
This data justifies continued investment and identifies areas needing configuration adjustment.
Common Concerns and How I Address Them
Teams considering AI code review often raise predictable concerns. Here’s how I respond.
False Positives
AI will sometimes suggest changes that are not improvements. I manage this by:
- Configuration tuning to reduce noise
- Easy dismissal workflows for invalid suggestions
- Feedback mechanisms that improve model performance
- Setting reasonable expectations about AI limitations
I accept some false positives if true positives provide net value.
Developer Trust
Some developers resist AI feedback, viewing it as threatening or patronizing. I address this by:
- Positioning AI as assistant, not replacement
- Emphasizing time savings for human reviewers
- Involving developers in configuration decisions
- Celebrating catches that prevent real issues
I always emphasize that AI review supplements rather than replaces human judgment.
Security and Data Privacy
Sending code to external services raises legitimate concerns. I advise teams to:
- Evaluate vendor security certifications (SOC 2, ISO 27001)
- Review data retention and handling policies
- Consider self-hosted options for sensitive code
- Understand what code snippets are sent for analysis
For highly sensitive projects, I recommend on-premises tools or local models.
Cost Justification
AI review adds expense. I justify it through:
- Developer time saved in review cycles
- Bugs caught before production
- Reduced technical debt accumulation
- Security incident prevention
Even one prevented production incident often exceeds annual tool costs.
How I Implement AI Code Review
I use a phased rollout that reduces risk and builds confidence.
Phase 1: Pilot
I start with one team or project:
- Select a representative codebase
- Configure tool for that environment
- Gather feedback for two to four weeks
- Measure initial metrics
- Adjust configuration based on experience
Phase 2: Expand
I roll out to additional teams with lessons learned:
- Document configuration patterns that worked
- Create templates for common project types
- Train teams on effective use
- Establish organization-wide guidelines
Phase 3: Optimize
I refine based on broader usage data:
- Tune configurations reducing false positives
- Develop custom rules for organization patterns
- Integrate with other quality tools
- Measure and report on impact
In my experience, AI code review represents one of the clearest wins available from AI tooling for development teams. The combination of consistent analysis, natural language feedback, and workflow integration makes human reviewers more effective while catching issues that manual review might miss. Small teams benefit disproportionately by getting review coverage that their limited numbers could not otherwise provide.
